The Si7021 I2C Humidity and Temperature Sensor is a monolithic CMOS IC integrating humidity and temperature sensor elements, an analog-to-digital converter, signal processing, calibration data, and an I2C Interface. The Si7021 offers an accurate, low-power, factory-calibrated digital solution ideal for measuring humidity, dew-point, and temperature, in applications ranging from HVAC/R and asset tracking to industrial and consumer platforms.

Features
Precision Relative Humidity Sensor ± 3% RH (max), 0–80% RH
High Accuracy Temperature Sensor ±0.4 °C (max), –10 to 85 °C
0 to 100% RH operating range
Up to –40 to +125 °C operating range
Wide operating voltage – (1.9 to 3.6 V)
Low Power Consumption – 150 μA active current
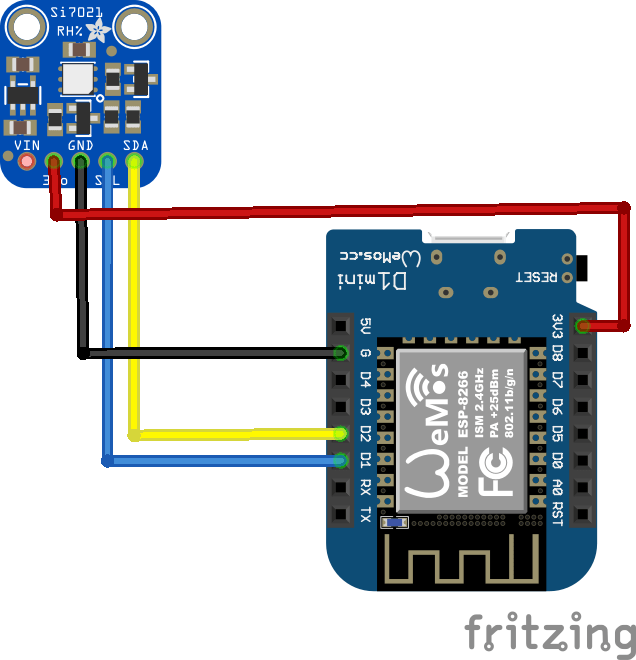
Connection
Code
No 3rd party libraries required
[codesyntax lang=”python”]
#include <Wire.h>
// SI7021 I2C address is 0x40(64)
#define si7021Addr 0x40
void setup()
{
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.beginTransmission(si7021Addr);
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(300);
}
void loop()
{
unsigned int data[2];
Wire.beginTransmission(si7021Addr);
//Send humidity measurement command
Wire.write(0xF5);
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(500);
// Request 2 bytes of data
Wire.requestFrom(si7021Addr, 2);
// Read 2 bytes of data to get humidity
if(Wire.available() == 2)
{
data[0] = Wire.read();
data[1] = Wire.read();
}
// Convert the data
float humidity = ((data[0] * 256.0) + data[1]);
humidity = ((125 * humidity) / 65536.0) - 6;
Wire.beginTransmission(si7021Addr);
// Send temperature measurement command
Wire.write(0xF3);
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(500);
// Request 2 bytes of data
Wire.requestFrom(si7021Addr, 2);
// Read 2 bytes of data for temperature
if(Wire.available() == 2)
{
data[0] = Wire.read();
data[1] = Wire.read();
}
// Convert the data
float temp = ((data[0] * 256.0) + data[1]);
float celsTemp = ((175.72 * temp) / 65536.0) - 46.85;
float fahrTemp = celsTemp * 1.8 + 32;
// Output data to serial monitor
Serial.print("Humidity : ");
Serial.print(humidity);
Serial.println(" % RH");
Serial.print("Celsius : ");
Serial.print(celsTemp);
Serial.println(" C");
Serial.print("Fahrenheit : ");
Serial.print(fahrTemp);
Serial.println(" F");
delay(1000);
}
[/codesyntax]
Testing
Open the serial monitor and you should see soemthing like this
Humidity : 50.55 % RH
Celsius : 22.20 C
Fahrenheit : 71.96 F
Humidity : 50.54 % RH
Celsius : 22.19 C
Fahrenheit : 71.94 F
Humidity : 50.96 % RH
Celsius : 26.13 C
Fahrenheit : 79.04 F
Humidity : 51.84 % RH
Celsius : 27.84 C
Fahrenheit : 82.11 F
Humidity : 53.12 % RH
Celsius : 27.97 C
Fahrenheit : 82.34 F
Link
GY-21 Humidity Sensor with I2C Interface Si7021 for Arduino


Hi,
How does Wire.begin get the “pin” values SDA and SCL to be 2 and 1 respectively for D2 and D0 GPIO of ESP8266?
Thanks
Its all to do with the pin definitions, for example the Wemos MIni one is at https://github.com/esp8266/Arduino/blob/master/variants/d1_mini/pins_arduino.h
If you look at the file you will see amongst other things the following
#define PIN_WIRE_SDA (4)
#define PIN_WIRE_SCL (5)
static const uint8_t SDA = PIN_WIRE_SDA;
static const uint8_t SCL = PIN_WIRE_SCL;
static const uint8_t D1 = 5;
static const uint8_t D2 = 4;